Omega-3s found to benefit a person’s behavioral and cognitive processes
04/14/2019 / By Michelle Simmons

Omega-3 fatty acids are believed to play a role in many different fundamental brain processes. These essential fatty acids have been associated with proper brain development and functioning of the central nervous system.
In a recent study published in the journal Food Science and Human Wellness, a team of researchers from the University of Regensburg in Germany sought to determine the effects of omega-3 deficiency on attention functions and impulsive behavior in rats. In addition, the research team looked at the effects of a diet that includes adequate omega-3 fatty acids in rats deficient on the nutrient on the same behavioral domains. The team found that omega-3 fatty acids indeed play a role in cognitive and behavioral processes. In particular, they found that adding omega-3 fatty acids to one’s diet improves attention and impulsive behavior.
In the study, the research team fed rats with an omega-3 deficient diet over several generations, and the dams of the seventh generation were randomly assigned to two diet groups and a received an omega-3 deficient or an omega-3 sufficient diet. In addition, they fed a group of previously untreated dams with an omega-3 sufficient diet. After these, the researchers assessed the attention and impulsive behavior of the male offspring of these three diet groups.
The results showed that the deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids over generations led to significant changes in the attention parameters and impulsive behaviors of rats. The treatment with the omega-3 sufficient diet also partially corrected the impairments associated with an omega-3 deficiency.
The findings of this study suggest that the detrimental effects of transgenerational of omega-3 deficiency can be at least partly reversed by feeding an omega-3 sufficient diet to dams and their offspring. This supports earlier animal studies that showed supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids can help in the recovery from behavioral deficits, such as impairments in spatial performance, avoidance, anxiety, or activity induced by a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) deficiency.
Other benefits of omega-3s on the brain
Omega-3 fatty acids also provide the following brain health benefits:
- Fighting depression and anxiety: Research has shown that taking omega-3 supplements or consuming dietary sources of omega-3s regularly helps fight depression and anxiety. Out of the three types of omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) was found to be the most effective at reducing the symptoms of depression.
- Promoting brain health during pregnancy and early life: Getting enough amounts of omega-3 fatty acids is important during pregnancy and infancy for the brain growth and development of children. Supplementing with omega-3s is associated with higher intelligence, better communication and social skills, fewer behavioral problems, and reduced risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, and cerebral palsy in children.
- Reducing ADHD symptoms in children: Studies have revealed that children with ADHD have lower than normal levels of omega-3 fatty acids, and that supplementing with omega-3s can reduce their symptoms of ADHD. In particular, these essential fatty acids improve attention and decrease hyperactivity, impulsiveness, and aggression.
- Improving mental disorders: Similar to children with ADHD, individuals with psychiatric disorders tend to have low omega-3 levels. Studies have found that improving omega-3 status can reduce the frequency of mood swings and relapses in people with both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, and reduce violent behavior.
- Preventing age-related mental decline: There is also evidence that omega-3s can help slow or decrease age-related mental decline and reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. (Related: Omega-3 benefits for brain health are well documented; now researchers have determined they help prevent Alzheimer’s.)
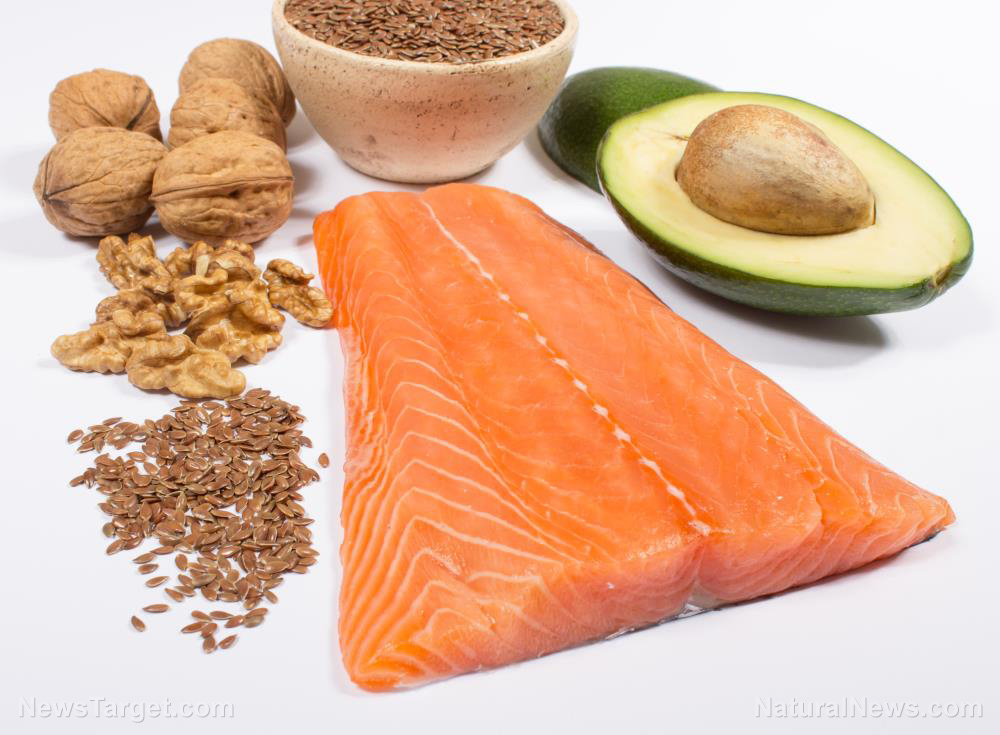
You can get omega-3 fatty acids from nuts, seeds, fish, seaweed, and algae. Nuts and seeds like chia seeds, hemp seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts are loaded with alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), while fatty fish like mackerel and salmon, seaweed, and algae provide docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and EPA fatty acids. Omega-3s are also available in supplement form.
Read more news stories and studies on the brain health benefits of omega-3s fatty acids by going to Omega3.news.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
attention, behavior, brain function, brain health, brain nutrients, cognitive function, Diets, fatty acids, impulsive behavior, omega-3 fatty acids, omega-3s, polyunsaturated acids, PUFAs, research, supplements
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
AntiAgingScience.News is a fact-based public education website published by Anti Aging Science News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Anti Aging Science News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.